BBC NEWS | Science & Environment | Single molecule’s stunning image.
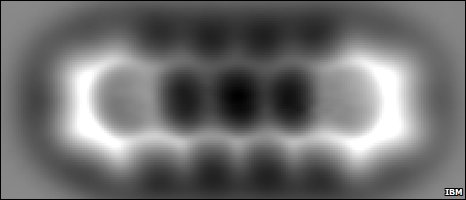
The detailed chemical structure of a single molecule has been imaged for the first time, say researchers.
The physical shape of single carbon nanotubes has been outlined before, using similar techniques – but the new method even shows up chemical bonds.
Understanding structure on this scale could help in the design of many things on the molecular scale, particularly electronics or even drugs.

Technology Review: The Smallest Laser Ever Made.
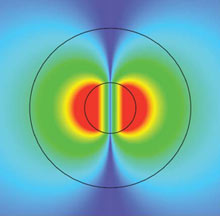
Researchers have demonstrated the smallest laser ever, consisting of a nanoparticle just 44 nanometers across. The device is dubbed a “spaser” because it generates a form of radiation called surface plasmons. The technique allows light to be confined in very small spaces, and some physicists believe that spasers could form the basis of future optical computers just as transistors are the basis of today’s electronics.
BBC NEWS | Science & Environment | A step closer to ‘synthetic life’.
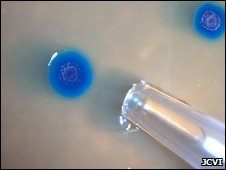
In what has been described as a step towards the creation of a synthetic cell, scientists have created a new “engineered” strain of bacteria.
A team successfully transferred the genome of one type of bacteria into a yeast cell, modified it, and then transplanted into another bacterium.
This paves the way to the creation of a synthetic organism – inserting a human-made genome into a bacterial cell.
DailyTech – Flexible LED Breakthrough Allows Bus-size Displays.
Reuters reports that researchers announced this week that they have devised a new way to make large-scale flexible displays that can be fitted to the contours of a bus, but are transparent. This would allow for video advertising on the displays, but passengers in the bus could still see out the windows.
DailyTech – Bionanoelectronic Devices Could Speed Up Electronics, Processing.
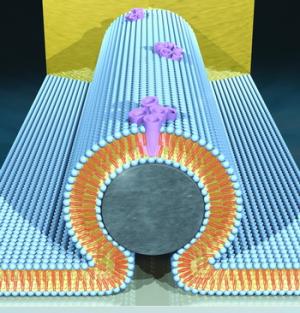
Mixing living cells with microscopic electronics may yield a new breed of processing power.
Though computer engineers and scientists have been repeatedly breaking speed barriers with new supercomputers, they still pale in comparison to the information processing power of complex biological systems. IBM’s Roadrunner supercomputer, presently the fastest in the world, has been used to mimic a single part of brain function, the visual cortex, and that’s only a fragment of the information the human body processes at any given moment.
So when researchers look to the future of computing, attempting to mimic bio-functions or combine them with electronics seems like a step in the right direction as far as speed and efficiency are concerned. However, the reality of the situation is not so supportive. Past attempts to merge the two types of systems have not yielded any special results.
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory scientists are taking a deeper, or more nanoscopic, look into the idea of cohabitating the living and the inanimate. “With the creation of even smaller nanomaterials that are comparable to the size of biological molecules, we can integrate the systems at an even more localized level,” explains Aleksander Noy, lead LLNL scientist on the bio-electrical project.
DailyTech – Researcher Discovers New Cloaking Method.
New method could hide buildings from earthquakes or tsunamis
A researcher for the University of Utah named Graeme Milton has developed a new cloaking method that may someday allow buildings and other large objects to be shielded from things like sonar, radar, earthquakes, and even tsunamis.
DailyTech – IBM Using DNA to Create Semiconductors Below 22nm.
Microprocessors using DNA construction are ten years away
The breakthrough uses DNA, the building blocks of the human body, as the starting point for microprocessors built at under 22nm size. The semiconductor industry is facing significant hurdles in developing lithographic construction processes for under 22nm construction. Research is also being done into incorporating carbon nanotubes or silicon nanowires into construction processes.
The smaller a semiconductor can be built, the cheaper the parts are to produce as well because more can be made on a single wafer.
Researchers at IBM have made a breakthrough that involves using DNA molecules as a scaffolding to build semiconductors. The so-called DNA origami structures are compatible with lithographic processes used in construction today. The DNA scaffolding approach allows IBM to place millions of carbon nanotubes that self assemble precisely into patterns by sticking to the DNA molecules.

DailyTech – Organic Electronics Vastly Improved with New Breakthrough.
New breakthrough in organic electronics transports electrons and holes with one layer
The creation of organic circuits that could conduct holes and electrons before the team’s breakthrough required a complex design with two patterns on top of each other. One pattern transported holes and the other transported electrons.
The new process creates a circuit that is able to transport holes and electrons is very fast. Electrons moved five to eight times faster in the new circuit and it produced a voltage gain two to five times greater than previously seen in a polymer circuit.

BBC NEWS | Science & Environment | Antarctic glacier ‘thinning fast’.
One of the largest glaciers in Antarctica is thinning four times faster than it was 10 years ago, according to research seen by the BBC.
A study of satellite measurements of Pine Island glacier in west Antarctica reveals the surface of the ice is now dropping at a rate of up to 16m a year.
Since 1994, the glacier has lowered by as much as 90m, which has serious implications for sea-level rise.
Calculations based on the rate of melting 15 years ago had suggested the glacier would last for 600 years. But the new data points to a lifespan for the vast ice stream of only another 100 years.
The rate of loss is fastest in the centre of the glacier and the concern is that if the process continues, the glacier may break up and start to affect the ice sheet further inland.
One of the authors, Professor Andrew Shepherd of Leeds University, said that the melting from the centre of the glacier would add about 3cm to global sea level.

BBC NEWS | Americas | Praying man let his daughter die.
A US jury has found a man guilty of killing his sick 11-year-old daughter by praying for her recovery rather than seeking medical care.
The man, Dale Neumann, told a court in the state of Wisconsin he believed God could heal his daughter.
She died of a treatable disease.
During the trial, medical experts told the court that Neumann’s daughter could have survived if she had received treatment, including insulin and fluids, before she stopped breathing.
On Thursday Neumann, who is 47 and studied in the past to be a Pentecostal minister, said he thought God would heal his daughter.
“If I go to the doctor, I am putting the doctor before God,” he said. “I am not believing what he said he would do.”
Neumann’s lawyer said he had been convinced that his “faith healing” was working, and that he had committed no crime.
DailyTech – Researchers Take a Step Forward in the Development of Transparent Aluminum.
Researchers claim to create a new state of matter never before seen on Earth
Oxford University researchers used a soft X-ray laser to create a new transparent aluminum, though it was transparent for just a fraction of a nanosecond.
Using a FLASH laser able to utilize fast pulses of soft X-ray light, the radiation is said to be ten billion times brighter than other high-power devices. The energy generated by the FLASH laser could have powered a small city.
The powerful beam caused the aluminum to become transparent for a total of 40 femtoseconds, which is only a fraction of a nanosecond, though is a sign of things to come. Furthermore, all of the power was directed to a location on the aluminum that had a diameter less than a twentieth of the width of a single strand of human hair.
BBC NEWS | Europe | Catholic bank owned pill shares.
A Roman Catholic bank in Germany has apologised after admitting it bought stocks in defence, tobacco and birth control companies.
Der Spiegel newspaper discovered the bank had invested 580,000 euros (£495,310, $826,674) in British arms company BAE Systems.
It also invested 160,000 euros in American birth control pill maker Wyeth and 870,000 euros in tobacco companies.
The bank apologised for behaviour “not in keeping with ethical standards”.
Pax Bank has previously advertised ethical investment funds, specifically claiming to avoid arms and tobacco companies along with organisations that do not adhere to Catholic beliefs.
The Catholic Church has historically condemned the use of contraception, for breaking the link between sex and procreation – a view emphatically upheld by current Pope Benedict XVI.
In the past he has called birth control a “grave sin”.
BBC NEWS | Technology | Artificial brain ’10 years away’.
A detailed, functional artificial human brain can be built within the next 10 years, a leading scientist has claimed.
Henry Markram, director of the Blue Brain Project, has already simulated elements of a rat brain.
The Blue Brain project at Swizerland’s EPFL (École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne) was launched in 2005 and aims to reverse engineer the mammalian brain from laboratory data.
In particular, his team has focused on the neocortical column – repetitive units of the mammalian brain known as the neocortex.
The project now has a software model of “tens of thousands” of neurons – each one of which is different – which has allowed them to digitally construct an artificial neocortical column.
Although each neuron is unique, the team has found the patterns of circuitry in different brains have common patterns.
To make the model come alive, the team feeds the models and a few algorithms into a supercomputer.
“You need one laptop to do all the calculations for one neuron,” he said. “So you need ten thousand laptops.”
Instead, he uses an IBM Blue Gene machine with 10,000 processors.
For example, they can show the brain a picture – say, of a flower – and follow the electrical activity in the machine.
















Recent Comments